In the evolving field of digital design, user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) designers play an important role in understanding how people interact with technology. These professionals create visually appealing and intuitively navigable digital products. We will explore the many facets of UI/UX design in this extensive book, looking at the UI/UX Designer Roles and Responsibilities that make up this exciting area of study.
Understanding the Basics:
To understand the UI/UX Designers roles and responsibilities, it’s essential to know the fundamental concepts of UI and UX.
UI Design:
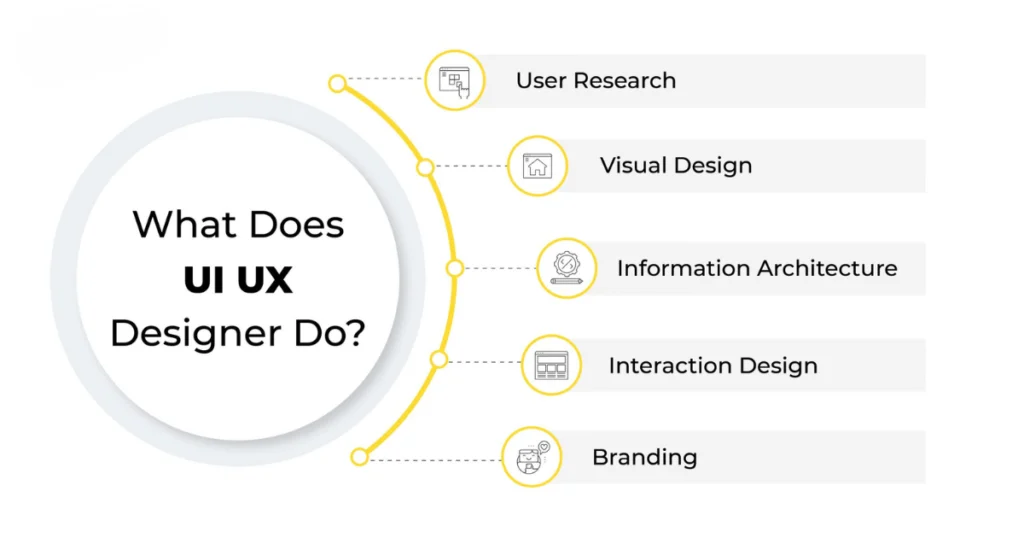
Visual Design: The role of UI designers is to produce attractive interfaces that are consistent with the brand’s identity. Choosing color schemes, fonts, and images that improve the overall design is part of this.
Layout Design: While designing a digital product’s layout, components must be arranged to maximize user engagement. To guarantee a smooth user experience, UI designers give much thought to where buttons, menus, and other elements are placed.
Interaction Design: Users’ interactions with the interface are the main focus of UI designers. In order to give users a responsive and interesting experience, interactive components like buttons, sliders, and input fields must be designed.
UX Design:
User Research: Understanding the target audience is a fundamental aspect of UX design. UX designers conduct extensive user research to identify user needs, preferences, and pain points.
Information Architecture: For a user to have a good experience, information must be organized logically and easily. UX designers organize content in such a way that consumers can easily browse and locate what they need.
Wireframing and Prototyping: UX designers use wireframes and prototypes to see how a digital product will look and work before the real design process begins. This technique supports the development of the design based on user feedback.

UI/UX Designer Roles and Responsibilities:
Roles and Responsibilities
Visual Branding: UI designers establish and maintain the visual identity of a product or brand across all digital platforms.
Style Guide Creation: Developing and maintaining a style guide ensures consistency in design elements, including colors, typography, and iconography.
Asset Production: UI designers are responsible for creating graphical assets such as icons, buttons, and images that enhance the overall visual appeal of the interface.
Collaboration with Developers: UI designers ensure that design elements integrate easily into the finished product by working closely with developers and taking technical limitations and opportunities into account.
UX Designer Roles & Responsibilities:
User Persona Development: Crafting detailed user personas helps in understanding the target audience and tailoring the design to meet their specific needs and expectations.
Usability Testing: Usability testing is a tool used by UX designers to assess a product’s usability. Iterative improvements and feedback collection are part of this process.
Journey Mapping: Mapping out the user’s journey from the initial interaction to the completion of a task helps in identifying pain points and areas for improvement.
Collaboration with Stakeholders: UX designers collaborate with product managers, developers, and other stakeholders to align design decisions with business goals and user needs.
The Intersection of UI and UX:
While UI and UX designers have distinct roles, there is a significant overlap between their responsibilities. This synergy is crucial for delivering a holistic and effective digital experience.
Collaboration:
Cross-functional Teams: UI/UX designers often work in cross-functional teams, collaborating with researchers, developers, and product managers to ensure a cohesive and user-centered design approach.
Iterative Design Process: Both UI and UX designers engage in an iterative design process, continuously refining and enhancing the digital product based on user feedback and evolving requirements.

UI UX Design Tools and Technologies:
Design Tools:
UI/UX designers use a variety of design tools such as
- Sketch
- Figma
- Adobe XD
User Testing Platforms: Implementing user testing platforms like Usertesting.com or UserZoom allows designers to gather valuable insights into user behavior and preferences.
Evolving Trends in UI/UX Design:
To excel in their roles, UI/UX designers must stay abreast of the latest trends and technologies shaping the design landscape.
Responsive Design:
Mobile-First Approach: With the increasing use of mobile devices, UI/UX designers prioritize designing for smaller screens first and then scaling up for larger screens.
Adaptive Design: Creating interfaces that adapt seamlessly to various devices and screen sizes ensures a consistent user experience across platforms.
Dark Mode:
User Preference: Dark mode has gained popularity due to its aesthetic appeal and the perceived reduction of eye strain. UI designers must consider incorporating this feature into their designs.
Voice User Interface (VUI):
Conversational Design: As voice-activated devices become more prevalent, UX designers are exploring conversational design principles to create intuitive and user-friendly voice interfaces.
Challenges and Future Outlook:
While UI/UX design has evolved significantly, designers face certain challenges in meeting user expectations and adapting to technological advancements.
Accessibility:
Inclusive Design: Designing interfaces that are accessible to users with diverse abilities is a priority. UI/UX designers need to consider factors like color contrast, text size, and screen reader compatibility.
Emerging Technologies:
AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning into UX design can enhance personalization and predictive capabilities, presenting new challenges and opportunities for designers.
Continuous Learning:
Lifelong Learning: UI/UX designers must adopt a mindset of continuous learning to stay relevant in a field that evolves rapidly. Keeping abreast of emerging technologies and design trends is crucial.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, UI/UX designers are essential to creating attractive and engaging digital experiences for people. They are responsible for everything from designing attractive interfaces to carrying out user research and testing. The dynamic and always changing nature of this sector is attributed to the creative nature of UI/UX design, the incorporation of developing trends, and the problems presented by these technologies. UI/UX designers will continue to be at the forefront of technological advancements, influencing how people interact with the digital world.






Leave a Reply